【導(dǎo)讀】在傳感器使用中,我們常常需要對(duì)傳感器數(shù)據(jù)進(jìn)行各種整理,讓應(yīng)用獲得更好的效果,以下介紹幾3種常用的簡(jiǎn)單處理方法。
◆ 加權(quán)平滑:平滑和均衡傳感器數(shù)據(jù),減小偶然數(shù)據(jù)突變的影響;
◆ 抽取突變:去除靜態(tài)和緩慢變化的數(shù)據(jù)背景,強(qiáng)調(diào)瞬間變化;
◆ 簡(jiǎn)單移動(dòng)平均線:保留數(shù)據(jù)流最近的K個(gè)數(shù)據(jù),取平均值。
01加權(quán)平滑
使用算法:(新值)=(舊值)×(1-a)+X×a
其中,a為設(shè)置的權(quán)值,X為最新數(shù)據(jù)。
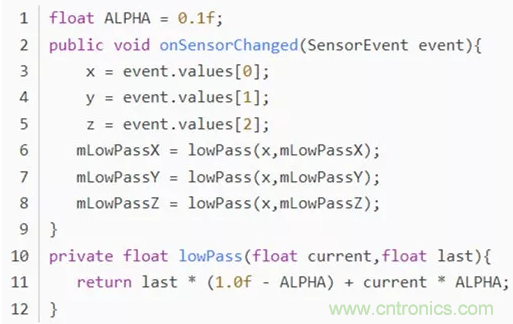
實(shí)現(xiàn)代碼如下:
02抽取突變
采用上面加權(quán)平滑的逆算法。
實(shí)現(xiàn)代碼如下:

03簡(jiǎn)單移動(dòng)平均線
保留傳感器數(shù)據(jù)流中最近的K個(gè)數(shù)據(jù),返回它們的平均值。其中,K表示平均“窗口”的大?。?/div>


實(shí)現(xiàn)代碼如下:


作者:羽凌寒
來源:https://blog.csdn.net/u011630458/article/details/22273147